The Complex Dynamics of Money Supply and Inflation
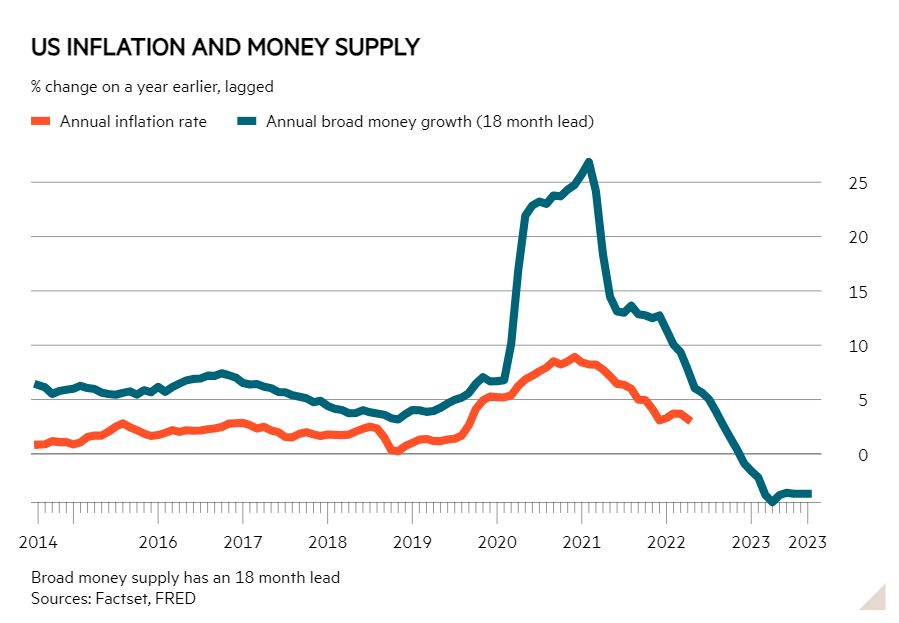
Recent trends in the money supply in major economies like the US and the eurozone, which have seen significant contractions, suggest a potential shift in future inflation rates. Economic analysts are debating the implications, as the conventional wisdom—that a reduced money supply leads directly to lower inflation—may not hold in the current global economic context. This situation presents a critical juncture for central banks as they consider the future of monetary policy and its impact on economic stability.
Navigating Uncertain Economic Waters
As evidenced by historical data, there is a notable correlation between changes in the money supply and inflation rates that typically manifest within a year to fifty days. However, the prediction that a continuing reduction in money supply could lead to a sharp decrease in prices remains contentious. Central banks are faced with the challenge of maintaining “higher for longer” interest rates, which, while aimed at tempering business cycles, could inadvertently hamper economic recovery if not aligned with actual business conditions.
The Role of Central Banks in a Shifting Economic Landscape
The relationship between the money supply and inflation is nuanced and influenced by various economic factors, including fiscal policies and market readiness to respond to changes in interest rates. Central banks are urged to carefully monitor the evolving situation, as premature adjustments could either fail to control inflation or stifle economic growth. The ongoing debates among economists underscore the complexities of predicting inflation and the critical role of timely and measured responses by monetary authorities in safeguarding economic stability.