Financial literacy is increasingly recognized as essential, not a luxury. A study by the National Financial Educators Council highlighted a concerning trend: Americans lacking in financial knowledge lose an average of $1,819 each year. Though this amount may seem modest initially, the cumulative effect over time—compounded by escalating living costs and potential for poor financial decisions—can be significant.
The Current State of Financial Literacy
In 2024, the need for financial literacy has become more acute amid a dynamic economic landscape and complex financial markets. Data from CivicScience indicates a decline in self-reported financial literacy from the previous year, underscoring an ongoing challenge: while financial resources are more accessible than ever, actual understanding hasn’t seen corresponding improvement. As of January, only 29% of U.S. adults consider themselves ‘very’ financially literate, a slight decrease from 2023, and those claiming no literacy at all increased to 12%.
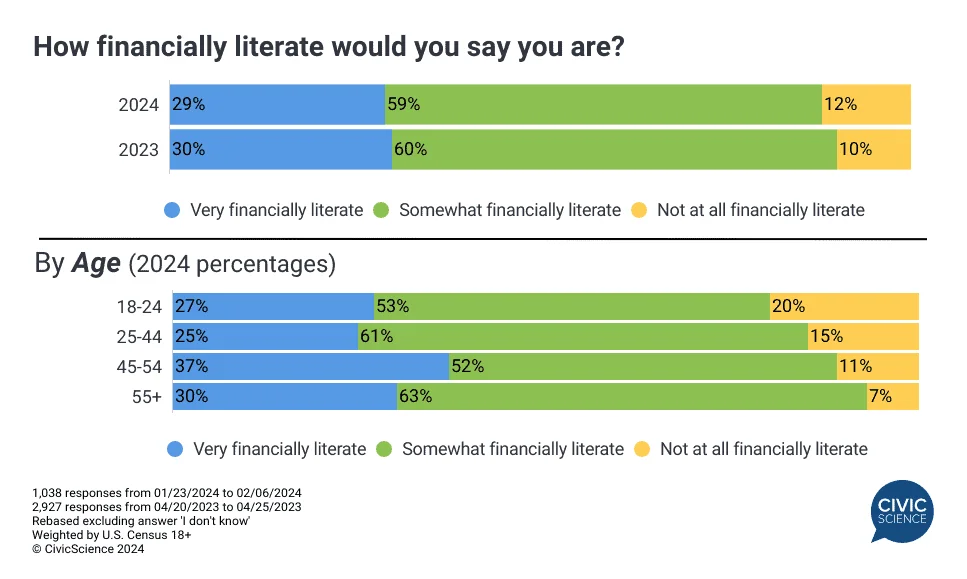
Financial literacy generally improves with age, yet young adults, especially Gen Z aged 18-24, struggle significantly, with one in five rating themselves as not at all literate. This contrasts with older generations, particularly Gen Xers, who demonstrate higher literacy. These findings underscore the importance of intensifying financial education efforts, particularly for younger demographics.
Financial Stress and Its Implications
Linking financial literacy to stress, studies show that a lack of financial understanding correlates strongly with increased financial stress. Those who are not financially literate are much more likely to report experiencing stress, with managing everyday living expenses being a predominant concern. This stress is not only more pronounced among the financially illiterate but also spans various financial aspects from debt management to credit scores.
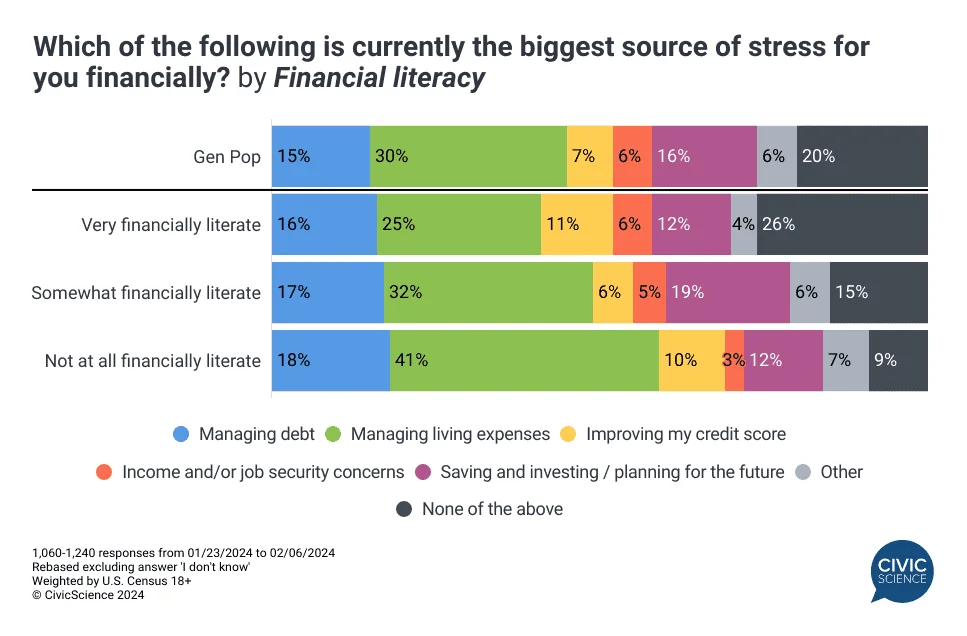
In 2024, financial stress related to daily expenses like rent and groceries has risen, with 30% of consumers reporting increased stress, up from 26% in 2023. There’s also a heightened focus on improving credit scores and a shift in the stress associated with saving and investing.
Bridging Financial Literacy and Security
Financial security remains elusive for many, with less than a third of Americans feeling completely financially secure. A close look at the data reveals a direct correlation between financial literacy and perceived financial security. Those lacking financial literacy are significantly less likely to feel secure, suggesting that enhanced financial knowledge is critical to fostering financial confidence and stability.
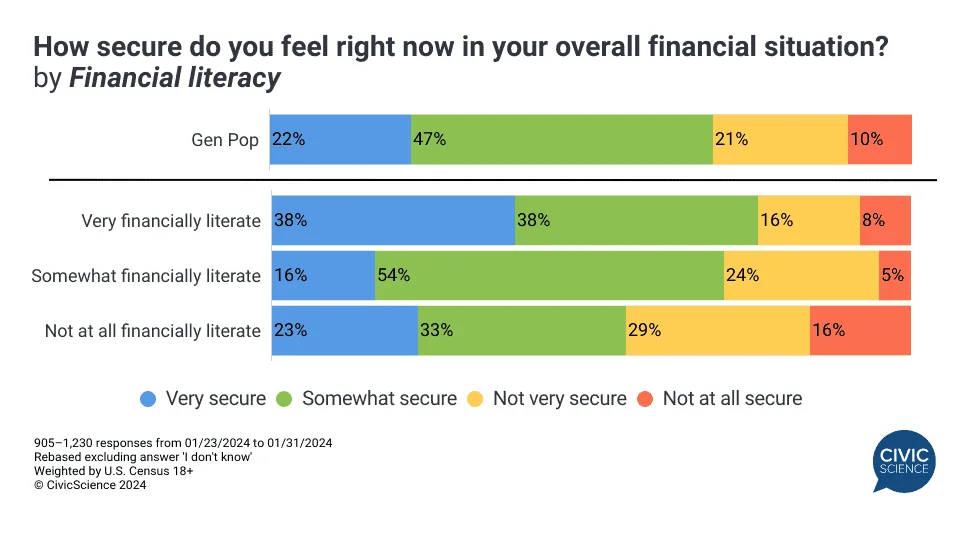
Moreover, the impact of financial literacy extends beyond immediate financial concerns, influencing long-term planning and perceptions of debt and savings adequacy. Individuals who are not financially literate are also more likely to overestimate their financial management skills, which can lead to adverse outcomes.
To combat these trends, it’s clear that enhancing financial literacy is not just beneficial but essential. As economic conditions evolve, empowering individuals through education will be key to improving both personal and broader economic well-being.

